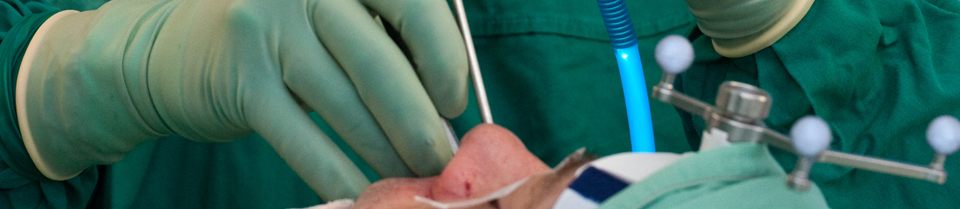
Laryngeal Dystonia (Spasmodic Dysphonia)
Laryngeal dystonia is a movement disorder of the muscles within the larynx, which most commonly manifests as spasmodic dysphonia (SD). Rarer reported manifestations include dystonic respiratory stridor (noisy breathing) and paroxysmal coughing. Laryngeal dystonia has been treated successfully with botulinum neurotoxin injections since 1984.
Laryngeal dystonia manifested as spasmodic dysphonia (92.7%), stridor (11.9%), dystonic cough (6.2%), dyscoordinate breathing (4.1%), paroxysmal hiccups (1.6%) and paroxysmal sneezing (1.6%). There were more females (68.4%) than males (31.6%). Average age at onset was 47 years. A positive family history of a dystonic syndrome was present in 16.1% of cases.
BOTOX injections are very effective across all subgroups. Severe adverse events are rare.
See also St Vincent's Voice and Swallowing Courses for clinicians.
